In fact, a major review this week of 247 studies, working out how much each risk factor, if dealt with, could reduce Alzheimer’s incidence, concludes that 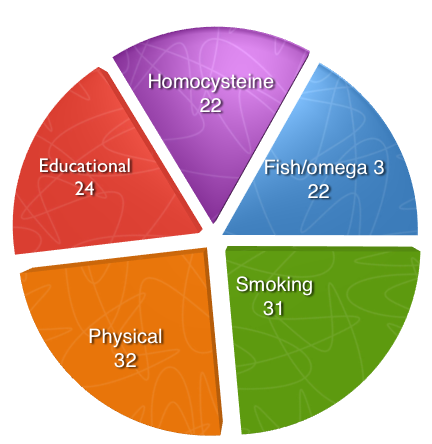 “The strongest evidence thus far is an increased risk of elevated plasma homocysteineHomocysteine is an amino acid found in the blood. Elevated levels of homocysteine have been associated with narrowing and hardening of the arteries, an increased… or lower educational attainment and a lowered risk with increased physical activity.” The authors estimate that “on average, one in five to one in three cases of Alzheimer’s disease can potentially be averted if those risk factors were eliminated from populations.”
“The strongest evidence thus far is an increased risk of elevated plasma homocysteineHomocysteine is an amino acid found in the blood. Elevated levels of homocysteine have been associated with narrowing and hardening of the arteries, an increased… or lower educational attainment and a lowered risk with increased physical activity.” The authors estimate that “on average, one in five to one in three cases of Alzheimer’s disease can potentially be averted if those risk factors were eliminated from populations.”
Their analysis finds that having a high homocysteine level, compared to a lower level almost doubles the risk of developing Alzheimer’s and accounted for 22% of Alzheimer’s disease in the population; that low fish intake versus high fish consumption accounted for 22%; having a high intake of omega 3 fatty acids significantly lowered risk; smoking in mid-life accounted for 31%; low physical activity versus high accounted for 32%, while low educational attainment accounted for 24% of Alzheimer’s disease. These risk factors can be reduced by testing and lowering high homocysteine (above 10mcmol/L) with B vitamins, increasing intake of omega 3 with fish oil supplements and eating more fish, not smoking and exercising. A combination of these factors could, the estimate, eliminate one third of Alzheimer’s cases.
This extremely positive news comes on the heels of an announcement by the Office of Health Economics that a treatment that could delay dementia by five years would cut the number of people with dementia by a third, with an annual saving of £21 billion by 2050. Although pharmaceutical interests are using this analysis to call for more money for drugs, there are now several trials that have shown that high dose B vitamins (B12, folic acidWhat it does: Critical during pregnancy for the development of a baby’s brain and nerves. Also essential for brain and nerve function. Needed for utilising…, B6) already do this, substantially reducing the rate of brain shrinkage nine fold, substantially delaying or stopping further memory decline in those with ‘pre-dementia’ called mild cognitive impairment (MCI), at least in those with raised blood homocysteine levels (above 11mcmol/L) which is half the older population.
B vitamins are therefore a ‘treatment that works’ and could easily delay onset of dementia, or even eliminate it in combination with other prevention strategies. B vitamins are cheap, unpatentable and unprofitable and consequently a serious threat to potential revenue and dementia-related drug sales.
‘Expert’ group attempts to trash B vitamins for memory prevention
So, surprise surprise, also published this month is a big study from a well sounding ‘expert group, the B Vitamin Treatment Trialists Collaboration (VTT), which declares that B vitamins do lower homocysteine but do nothing for age-related memory decline.
On the face of it this meta-analysis of 11 trials of B vitamins, involving 22,000 individuals, looks like solid science. The conclusion “Homocysteine lowering by using B vitamins had no significant effect on individual cognitive domains or global cognitive function or on cognitive aging.” In other words, there was no change, no improvement or worsening in memory over 5 years.
Before showing the various ways meta-analyses like this can torture data to make it come up with the results you want, it’s worth filling in a bit of background of the VTT, which is related to, and modeled on the CTT (Cholesterol Treatment Trialists), a collaboration that has been very much in the news. The CTT stands accused of serious shortcomings in both biased selection of study participants, and not disclosing all the trial data, to create the impression of non-existent benefits for statins, plus the illusion of an absence of side effects. (For details on this read my blog). Professor Sir Rory Collins, a senior fellow in the CTT, and also an author of the VTT study, has been in the news for his heavy handed treatment of academic critics, accusing them of killing people by denigrating statins.
The reason this is relevant is that very similar tactics have been employed in the way the VTT trial has been done. Bearing these points in mind let’s dissect this recent study on B vitamins and memory, published in this month’s American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
How to kill off the competition
Step 1 – Even though it is not stated anywhere in the front page abstract, if you read carefully, tucked away on the last page, it says “Trials in persons selected on the basis of a prior diagnosis of Alzheimer disease or cognitive impairment or depression (28–30) were excluded because the effects of treatment in people with established cognitive impairment may differ from those in the general population.” In other words, no-one with potential memory issues were included. Also, any study that hadn’t completed by September 2010 was excluded. (The best studies have been in the last five years, not before then.) These therefore memory healthy people had to have been given B vitamins for at least three months, with an average overall all the trials of five years. For now, we will ignore the dose issue since studies used different doses and different combinations, but 3 months is far too short a time to expect an effect. It would have been far better science to stick to studies of one year or more.
Step 2 – One of the tests used to see if memory had got worse or better was the Mini Mental State Exam (MMSE). The trouble it’s a virtually useless test in looking for subtle changes in memory or cognition. The maximum MMSE score is 30. Most older people will average a score of 28. Your score would have to drop to 25 or below to be suspected of pre-dementia. If you take normal people they’d actually have to have a massive and rapid decline into pre-dementia to pick up a significant change on the MMSE within five years, let alone three months.. We know the MMSE declines, on average, by only 0.1 per year in healthy older people. So, in five years you’d expect a decline of no more than 0.5. But there are no half scores on the MMSE so you’d probably see nothing. So if, in normal ageing, your score drops from 28 to 27.5 you would report no meaningful change in cognition.
Guess what? There was no significant change in MMSE scores in those taking B vitamins. A much better test would be something like Food for the Brain’s Cognitive Function Test which sensitively measures the four critical aspects of cognition known to decline in those who develop pre-dementia.
Step 3 – But, you might wonder, even if the B vitamin takers had no improvement in their MMSE scores, what happened to those not on B vitamins, taking placebos? Of course we need to know. Well, the authors don’t tell you! This is an example of the non-disclosure of data that has got the CTT group into such deep trouble.
If, for example, the placebo takers’ MMSE scores got worse by 0.5, which is what you’d expect, but stayed the same in those taking B vitamins then you would say the B vitamins stopped or delayed memory decline, but didn’t actually improve memory. That’s kind of what you might expect or hope for. If they too stayed the same, even in the placebo group, you’d realise the memory test was just too insensitive. If, as is likely for normal elderly, the scores in those taking placebo, showed no significant decline over time, then of course you cannot expect B vitamins to slow decline. Come clean VTT – gives us your placebo results!
Step 4 – Now, the paper says that B vitamins did lower homocysteine levels by 26%, but didn’t change the memory scores. The implication here is that, yes, we concede that homocysteine may be a marker for dementia risk, and B vitamins do lower it, but they don’t improve memory, so homocysteine can’t be part of the cause. That’s a perfect argument for killing off further research on B vitamins and championing potential drugs. ‘Potential’ might be too strong a word because there are none, not one, in the pipeline that show any clinical evidence of benefit, except a tiny benefit in one study in those 1 per cent of Alzheimer’s sufferers, who develop it due to a very rare combination of genes. Around $50 billion spent without a single effective or marketable discovery!
Now, the VTT obviously have the homocysteine data – that’s how they worked out the 26% drop. But they don’t do the most obvious thing with that data, given that it is already established that those with mild cognitive impairment and homocysteine above 11mcmol/L get better on B vitamins.
That is to divide the study population into those starting with a high, medium or low homocysteine level. For example, while overall there was no significant improvement in MMSE scores what happened to those who started with higher homocysteine levels? This is such an obvious thing to do these intelligent people can’t surely have just not thought to do it? Come on VTT, use your homocysteine data!
Step 5 – Of course, if your aim is to kill off B vitamin treatment, and you know people are well aware of the positive studies with B vitamins, you can’t just pretend they don’t exist. You’ve got to say something, even if you find an excuse to not include them in your analysis, as VTT did by excluding any studies of anyone with memory problems.
Here’s how they do it. In the final page they say “the claims that lowering homocysteine can prevent cognitive aging (10, 36, 37) within just a few years of treatment are not supported by the present meta-analysis.” These are the three unquestionable studies (Durga, De Jager, Douaud and also Smith) that showed significant effects on memory in those given B vitamins. These were not ‘claims’. They were actual study results. These authors specifically showed that in those with raised homocysteine, supplementing B vitamins at the right dose both substantially slow cognitive decline and the rate of brain shrinkage. The VTT group are misrepresenting these studies. Was that a mistake or on purpose? What do you think?
I am personally appalled that the VTT, just like the CTT, think they can get away with such biased and incomplete manipulation of data! But the trouble is that 99% of people – media, policy makers and doctors – will just read the front page. And that’s the point. The hatchet job well done. The seed of doubt firmly sown, the effect of which is to keep the path clear for drugs and to delay as much as possible people who need it from receiving B vitamin treatment. It is, in my opinion, the immoral use of science.
If you would like us to keep sharing important findings with you, exposing the misuse of science, and demanding that government agencies put the right prevention policies in place please support Plan B.

Comments
Join the Conversation on our Facebook Page