The reason fruit and vegetables are so important to include in your diet and have such a strong association with good health is that they contain all kinds of compounds which support your health in different ways. You are likely to be familiar with antioxidants and perhaps polyphenols which reduce inflammation and disease risk, but they also contain salvestrols which ward off cancer and sirtuin activators which help burn fatThere are many different types of fats; polyunsaturated, monounsaturated, hydrogenated, saturated and trans fat. The body requires good fats (polyunsaturated and monounsaturated) in order to….
Some fruit and vegetables contain more of these compounds than others so in this article you’ll find out which ones contain the most so you can make the best choices for optimum health.

1. Fruit and vegetables rich in antioxidants
Fruit and vegetables are our most important source of antioxidants – helping to slow down oxidative damage in your body. Berries, plums, apples, oranges, broccoli, cabbage, asparagus, avocado and artichoke are top of my list for providing antioxidants. ORAC (oxygen radical absorption capacity) is the measure of the total antioxidantAntioxidants are substances that protect cells within the body from damage caused by free radicals. They help to strengthen the body’s ability to fight infection… power of fruit and vegetables. The chart below gives you some of the top ORAC star foods.
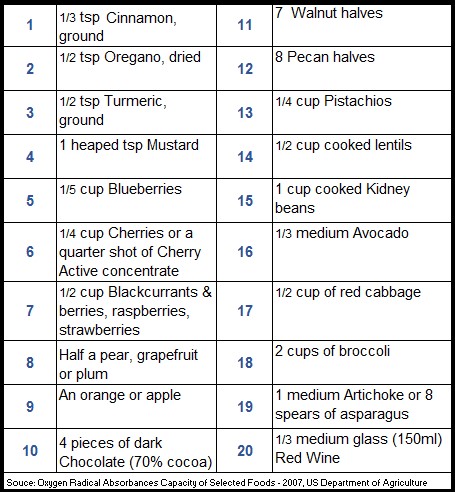
2. Which food provides polyphenols?
However as mentioned above, it’s not just the ‘antioxidant power’ you need to consider. There’s now been lots of research showing that a group of compounds known as ‘polyphenols’ are just as important and maybe more so. Polyphenols are rich in many ‘superfoods’ such as the resveratrol in red grape skin, isoflavonesIsoflavones are naturally occurring compounds – many act as phyto-oestrogens. An example of an isoflavone is Soya Isoflavones…. in beans, curcumin in turmeric, cinnamic acid in cinnamon, quercitin in onions and anthocyandins in berries.
Polyphenols are produced by plants as part of their defence system to protect the plant from infection or UV radiation. When we eat them they often protect us from infection and cancer, but they also seem to switch off disease processes and switch on healthy genetic switching that helps us stay healthy and live longer.
By seeing which foods have the most antioxidant power AND the most polyphenol power we can get a good idea of the best foods to include in our diet.
Since quite a few polyphenols act as antioxidants there is a tendency for a food to score high in both camps, but some foods don’t. Peppermint, for example, is good for polyphenols but not so remarkable as an antioxidant. Basil is the other way round – good for antioxidants, but not great for polyphenols. Here are the winners:
Best fruits and vegetables for both antioxidants and polyphenols
- Vegetables: artichoke, red onion, broccoli, asparagus, spinach, olives, beetroot, avocado, kale, parsley
- Fruits: blackcurrants, blueberries, plums, blackberries, raspberries, strawberries, cherries, apples
- Nuts: chestnuts, pecan nuts, almonds, chia, flax
- Herbs and spices: cloves, oregano, turmeric, capers, mint, star anise, sage, rosemary, basil, thyme, ginger, curry powder, cinnamon
- Other: dark chocolate, red wine, coffee, peppermint (tea), black tea, green tea

3. Where do you find ‘fat burning’ sirtuins?
Sirtuins are a plant compound that activate ‘skinny’ genes, helping you burn fat and build muscle. These include resveratrol in the red skin of grapes and peanuts, green tea, cocoa powder, turmeric, kale, onions, especially red onions, olives, parsley and lovage. While many fruits and veg do contain sirtuin activators the levels in common foods such as tomatoes, lettuce, kiwi, carrots and cucumber are relatively low.
4. Anti-cancer salvestrols
Salvestrols ward off cancer as they are activated only inside cancer cells, into compounds that can kill the cancer cell. They are found most abundantly in red and green fruits and vegetables, and are especially high in organic produce as use of fungicides dramatically reduces a plant’s production of salvestrols.
Salvestrols are often bitter tasting, so many of us don’t eat enough of the foods they are in, such as olives. The table below shows the 27 tested to date that are particularly good sources. It is important to realise that the Salvestrol concentration depends very much on where and how the plant is grown and the particular variety of fruit or vegetable.
Salvestrol rich fruit and vegetables:
| Fruits | Vegetables | Herbs |
| Apples | Aubergines | Basil |
| Blackcurrants | Artichokes (globe) | Dandelion |
| Blueberries | Avocado | Milk thistle |
| Cranberries | Broccoli | Mint |
| Grapes (& wine) | Brussels sprouts | Parsley |
| Oranges | Cabbage | Rosemary |
| Strawberries | Cauliflower | Sage |
| Tangerines | Olives | Thyme |
| Red/yellow peppers |

My all-round top dozen fruit and veg
My one concern with eating too much fruit, not vegetables, is the potential for taking in too much fructoseFructose is a simple sugar that occurs naturally in fruits, vegetables and their juices, as well as in honey…. or fruit sugar. Berries, cherries and plums, however, are both high in antioxidants and polyphenols, but very low in fructose, while grapes are high in antioxidants but also high in sugar.
Taking all these factors into account – the antioxidant, polyphenols, salvestrols and sirtuin activators – these are my dozen best rated fruit and veg. But do not think of this list as definite as more and more research reveals the amazing healing power of nature’s fruits and vegetables.
| Lowest GL | Antioxidant | Polyphenol | Salvestrol | Sirtuin Act. | |
| Olives | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| Blueberries | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** |
| Kale | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** |
| Blackcurrants | ** | *** | ** | *** | *** |
| Broccoli | *** | ** | *** | *** | |
| Artichokes | *** | ** | *** | *** | |
| Cabbage (red) | *** | *** | ** | *** | |
| Asparagus | *** | ** | ** | *** | |
| Onions (red) | ** | * | *** | *** | |
| Avocado | *** | ** | ** | *** | |
| Apples | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Beetroot | * | * | *** | ||
| Cherries | ** | ** | ** |
It is also important to eat turmeric, cinnamon, oregano, parsley, mint, basil, ginger, dark chocolate or cocoa and drink tea, ideally green.
In summary I’d suggest you aim for at least 7 servings of fruit and vegetables a day, including a variety of the foods suggested in this article, so as to get the health advantages of the various different plant compounds found in them.
To find out more about optimum nutrition – why and how it works – read The Optimum Nutrition Bible or if you want to cut to the case Optimum Nutrition Made Easy.

Comments
Join the Conversation on our Facebook Page